Agent¶
About RL Agent¶
The RL Agent class in DI-engine, as its name implies, functions as a direct surrogate for interaction with the environment during the training or evaluation process.
Once initialized, each RL Agent retains an environment, a policy instance, and its related configurations. All RL algorithms in DI-engine will be implemented as specific RL Agent classes, each equipped with the standard training or evaluation methods. The RL Agent class supports a wide range of classic RL benchmark environments including Gym Atari and Mujoco, ensuring the compatibility and versatility of the class.
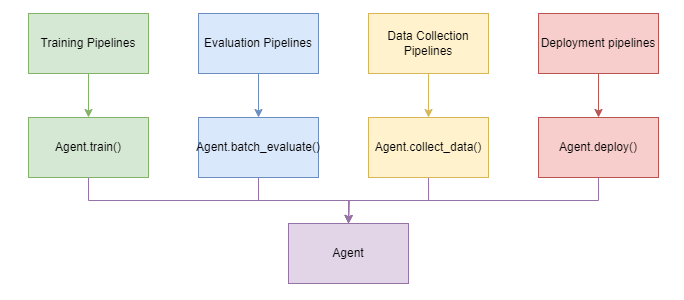
The RL Agent class provides an effective abstraction for RL pipelines. In particular, the RL Agent class includes four main methods: “train”, “deploy”, “batch_evaluate”, and “collect_data”. This abstraction allows for the combination of four distinct DI-engine pipelines into one class with four methods. This saves the previously required need of writing individual pipeline code into separate files. It solves the issue of inconsistency and confusion when users unfamiliar with reinforcement learning pipelines or DI-engine code have to train the PPO algorithm for some game environment and deploy the trained model for a video replay, necessitating the combination of the training and deployment pipelines or using the model checkpoint as an intermediary to run the pipelines separately. Thanks to the RL Agent class, a standard implementation to manage all operations is now available, allowing training and evaluation processes to be concatenated in any order or easily called by third-party pipelines.
Usage of RL Agent¶
The RL Agent class offers streamlined configurations for benchmark environments encountered in classic RL. These default settings have been extensively tested and deliver reliable performance. This makes it possible for new users to initiate the training process without requiring any prior information.
from ding.bonus import DQNAgent
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Initialize the agent
agent = DQNAgent(env_id="LunarLander-v2", exp_name="LunarLander-v2-DQN")
# Train the agent
return_ = agent.train(step=int(2000000))
# Deploy the agent and render a video replay
agent.deploy(enable_save_replay=True)
The RL Agent class also supports users to train RL agents using custom configurations. The configuration format can refer to the default configuration. For example, to use the DQN algorithm to train the LunarLander environment, you can refer to the file gym_lunarlander_v2.py <https://github.com/opendilab/DI-engine/blob/main/ding/config/example/DQN/ gym_lunarlander_v2.py>.
from ding.bonus import DQNAgent
from ding.config.example.DQN.gym_lunarlander_v2 import cfg
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Initialize the agent
agent = DQNAgent(exp_name="LunarLander-v2-DQN", cfg=cfg)
# Train the agent
return_ = agent.train(step=int(2000000))
# Deploy the agent and render a video replay
agent.deploy(enable_save_replay=True)
The RL Agent class integrates the training and evaluation pipelines, allowing users to call training and evaluation methods in the same main file without having to use multiple files to perform training and evaluation separately. In this way, users can evaluate the performance of the agent at any time during the training process, or train the agent at any time during the evaluation process.
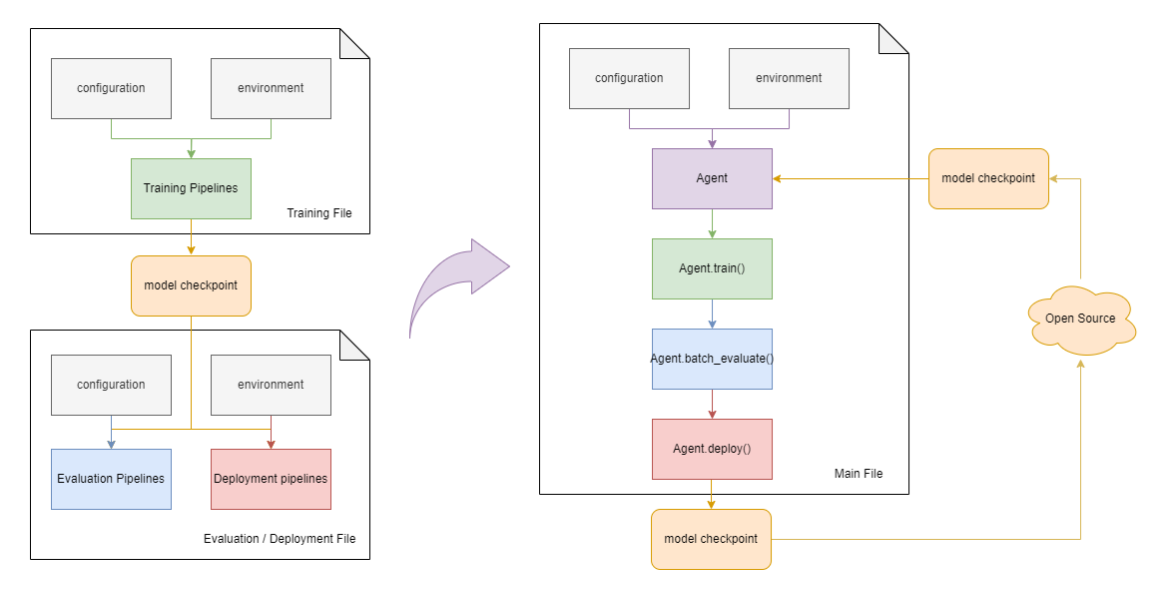
In addition, the trained model checkpoints are accessible on the Hugging Face Hub. To download these models, we kindly request you to follow the explicit instructions provided on the respective model card webpages. (Take for example the LunarLander-v2-DQN model, for more in-depth information about downloading and deployment, simply follow the given link.)