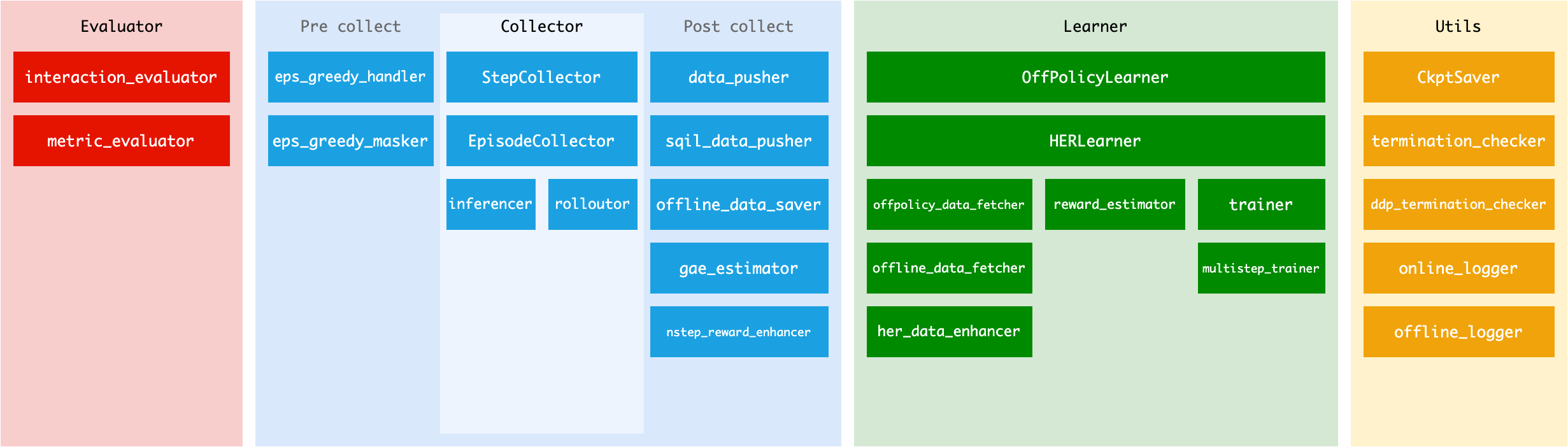
中间件¶
在大部分强化学习流程中,都存在着环境与智能体之间的「探索-利用」循环 —— 从环境中取得数据,训练智能体,取得更好的数据,周而复始。 我们将在后续的 DI-zoo 章节 中详细介绍各个环境的特性,这里将着重实现智能体的交互策略。
强化学习的复杂策略决定了它很难用对象抽象所有参与交互的实体,随着更好的策略和算法不断出现,新的概念和对象无穷无尽, 所以我们的主意是不做对象抽象,而只封装过程,并且力保这些封装后的代码可重用,可替换。这就产生了 DI-engine 的基础概念 —— 中间件。
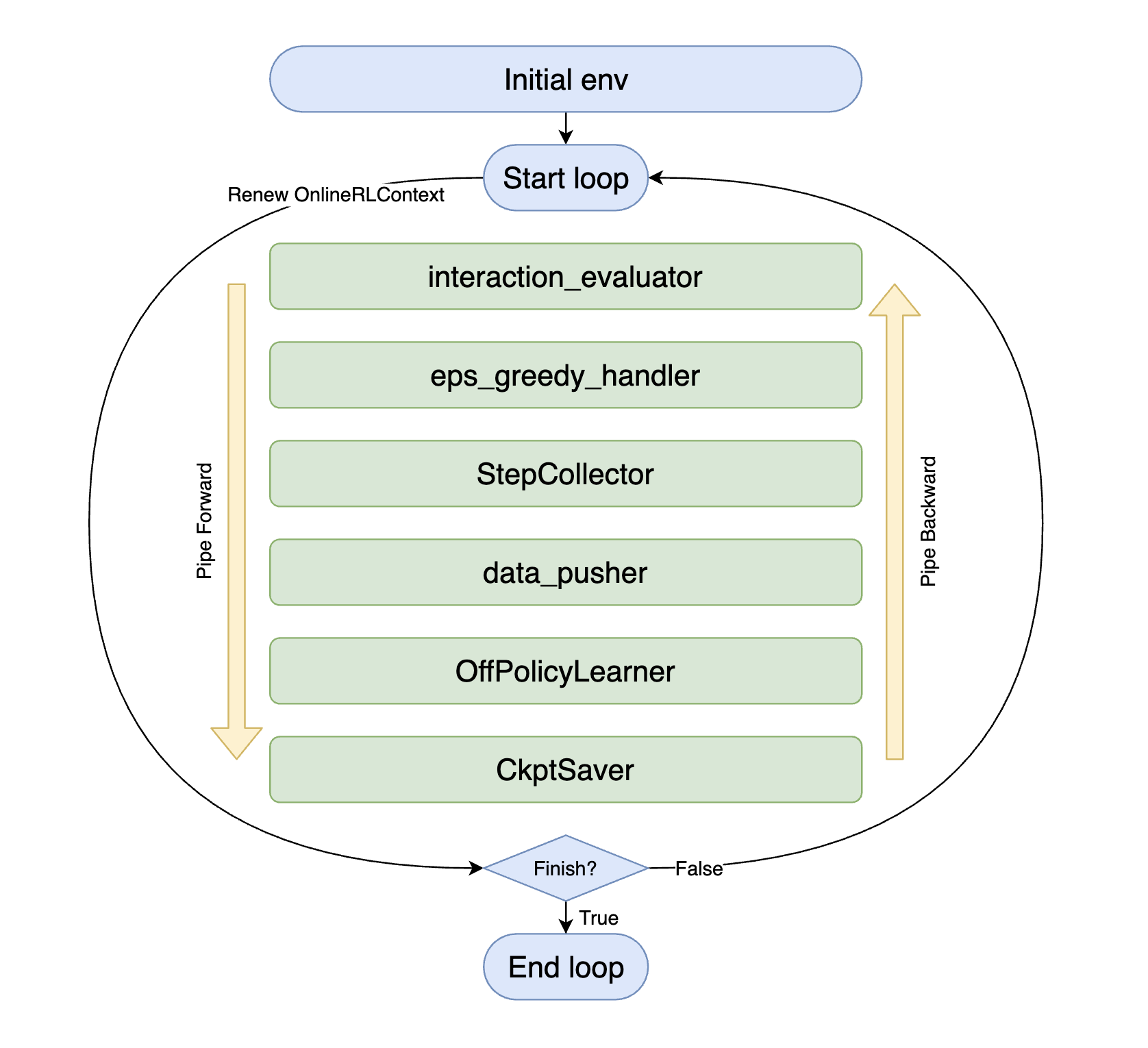
如上图所示,每个中间件(图中绿色部分)仅靠名字即可推测其用途,您仅需在 DI-engine 的 middleware 库中选择合适的方法,将它们组合起来,就完成了整个智能体的交互策略。
with task.start(async_mode=False, ctx=OnlineRLContext()):
task.use(interaction_evaluator(cfg, policy.eval_mode, evaluator_env))
task.use(eps_greedy_handler(cfg))
task.use(StepCollector(cfg, policy.collect_mode, collector_env))
task.use(data_pusher(cfg, buffer_))
task.use(OffPolicyLearner(cfg, policy.learn_mode, buffer_))
task.use(CkptSaver(policy, cfg.exp_name, train_freq=100))
task.run(max_step=100000)
熟悉了中间件的使用之后,您会发现原来强化学习的几大流派 —— Onpolicy, Offpolicy, Offline 等等居然在流程上会有这么多可复用部分, 通过简单的取舍,您就能将一个 Offpolicy 策略的交互流程改造为 Onpolicy 策略。
with task.start(async_mode=False, ctx=OnlineRLContext()):
task.use(interaction_evaluator(cfg, policy.eval_mode, evaluator_env))
task.use(StepCollector(cfg, policy.collect_mode, collector_env))
task.use(gae_estimator(cfg, policy.collect_mode))
task.use(multistep_trainer(cfg, policy.learn_mode))
task.use(CkptSaver(policy, cfg.exp_name, train_freq=100))
task.run(max_step=100000)
上下文对象(Context)¶
Context 是为中间件之间传递数据的信使,不同的交互策略决定了它们该使用什么类型的 context,
例如 DI-engine 中提供了 OnlineRLContext 和 OfflineRLContext 两种 context。
@dataclasses.dataclass
class OnlineRLContext(Context):
# common
total_step: int = 0
env_step: int = 0
env_episode: int = 0
train_iter: int = 0
train_data: Union[Dict, List] = None
...
def __post_init__(self):
self.keep('env_step', 'env_episode', 'train_iter', 'last_eval_iter')
OnlineRLContext 上面保存了在线训练所需要的数据,每个中间件的任务就是利用这些数据,并提交新的数据到 context 上面,
例如 OffPolicyLearner 中间件的任务就是利用 ctx.train_data 训练模型,并且将训练结果写回到 ctx.train_iter 上面。
在每个循环开始,context 会初始化为新的实例,这确保中间件只需关注一次循环内的数据流,简化了逻辑,也减少了内存泄漏的风险。
如果您需要保存属性到下一个循环,例如 env_step,train_iter 这类需要累加的数值,可以用 ctx.keep 方法将它设置为保留字段。 使用 ctx.keep 调用的字段将在新一轮迭代,context 初始化为新的实例时保留,而其他的字段将被重新初始化。 注意,理论上 ctx.keep 不需要,也不应该被用来保留那些集合类型的数据,或者比较复杂的类,比如 list,dict,torch.Tensor 或者 torch.nn.Module 等, 而只应该保存 int,float 等类型的数据到下一个迭代,如果需要的话。
注:__post_init__(self) 是在 __init__(self) 后被立刻调用的方法。在我们的 Context 中,这意味着在每一个字段初始化之后调用该方法。 我们将 self.keep 在该函数中调用,是因为我们需要先将每个字段初始化,才能调用 self.keep 来保留那些被选择的变量。
v0.4.2 更新 Context 到 dataclass¶
在 v0.4.2 版本 中,我们将 Context 从 dict 类改为 dataclass 类。 这个改动的原因是:
防止在开发过程中随意在 Context 中添加新字段,即 ctx 中的字段必须在定义时明确清楚;
防止使用者使用字符串去访问 Context 中的具体字段,即,禁止 ctx[‘xxx’]。
因为通过 Context 传递数据不同于通过函数的输入和输出传递数据,会有一个强制的约束。 随意在外部定义一个新的属性,或者使用字符串访问 Context 中的字段的话,很容易在阅读代码或者多人协作时造成混乱,在拼接不同中间件时报错。
通过将 Context 改为 dataclass 类,我们限定使用属性而不是字符串去访问 Context 中的具体字段,并且防止在外部添加新字段。 如果您需要在 Context 中添加新字段的话, 请在相关 Context 的 初始化阶段 添加。 下面是自定义 Context 的一个具体例子:
@dataclasses.dataclass
class MyContext(Context):
# common
total_step: int = 0
var1: int = 0
var2: int = 0
var3: Union[Dict, List] = None
var4: List = None
def __post_init__(self):
self.keep('var1', 'var2')
如果认为某新字段有必要添加到整个项目中的话,请向 DI-engine 的 main 分支提出 PR 并说明具体原因。
Context 字段介绍¶
注:Updated position 不包含 ctx.attribute = None 的情况。
OnlineRLContext¶
Attribute |
Keeped |
Type |
Role |
Updated position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
total_step |
True |
int |
The number of total iteration steps. |
In the beginning of each middleware execution loop. |
env_step |
True |
int |
The number of environment steps. |
rolloutor |
env_episode |
True |
int |
The number of environment episodes. |
rolloutor |
train_iter |
True |
int |
The number of training iterations. |
trainer, multistep_trainer |
train_data |
False |
Union[Dict, List] |
The fetched data used to be trained. |
gae_estimator, offpolicy_data_fetcher, offline_data_fetcher, her_data_enhancer |
train_output |
False |
Union[Dict, List[Dict]] |
The training output including logit, action and other info. |
OffPolicyLearner, HERLearner(List), trainer, multistep_trainer(Dict) |
collect_kwargs |
False |
dict |
The dict include epsilon value. |
eps_greedy_handler |
obs |
False |
ttorch.Tensor |
The input observations collected from all collector environments. |
inferencer |
action |
False |
List |
The inferred actions listed by env_id. |
inferencer |
inference_output |
False |
Dict[int, Dict] |
The dict of which the key is env_id (int), and the value is inference result (Dict). |
inferencer |
trajectories |
False |
list |
The trajectories collected from environment. |
StepCollector, nstep_reward_enhancer |
episodes |
False |
list |
The episodes collected from environment. |
EpisodeCollector |
trajectory_end_idx |
False |
list |
The end index of each trajectory in ctx.trajectories. |
StepCollector |
eval_value |
False |
float |
The average reward in the current evaluation. |
interaction_evaluator, metric_evaluator |
last_eval_iter |
True |
int |
The last ctx.train_iter that is evaluated. |
interaction_evaluator, metric_evaluator |
OfflineRLContext¶
Attribute |
Keeped |
Type |
Role |
Updated position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
total_step |
True |
int |
The number of total iteration steps. |
In the beginning of each middleware execution loop. |
train_epoch |
False |
int |
The count of training epoches. |
offline_data_fetcher |
train_iter |
True |
int |
The number of training iterations. |
trainer, multistep_trainer |
train_data |
False |
Union[Dict, List] |
The fetched data used to be trained. |
gae_estimator, offpolicy_data_fetcher, offline_data_fetcher, her_data_enhancer |
train_output |
False |
Union[Dict, List[Dict]] |
The training output including logit, action and other info. |
OffPolicyLearner, HERLearner(List), trainer, multistep_trainer(Dict) |
eval_value |
False |
float |
The average reward in the current evaluation. |
interaction_evaluator, metric_evaluator |
last_eval_iter |
True |
int |
The last ctx.train_iter that is evaluated. |
interaction_evaluator, metric_evaluator |
使用 task 异步执行任务¶
Task 是 DI-engine 用来管理强化学习交互任务的全局对象,所有的运行时状态都在 task 内维护,上面也提供了一些语法糖来帮助流程变得更简单。
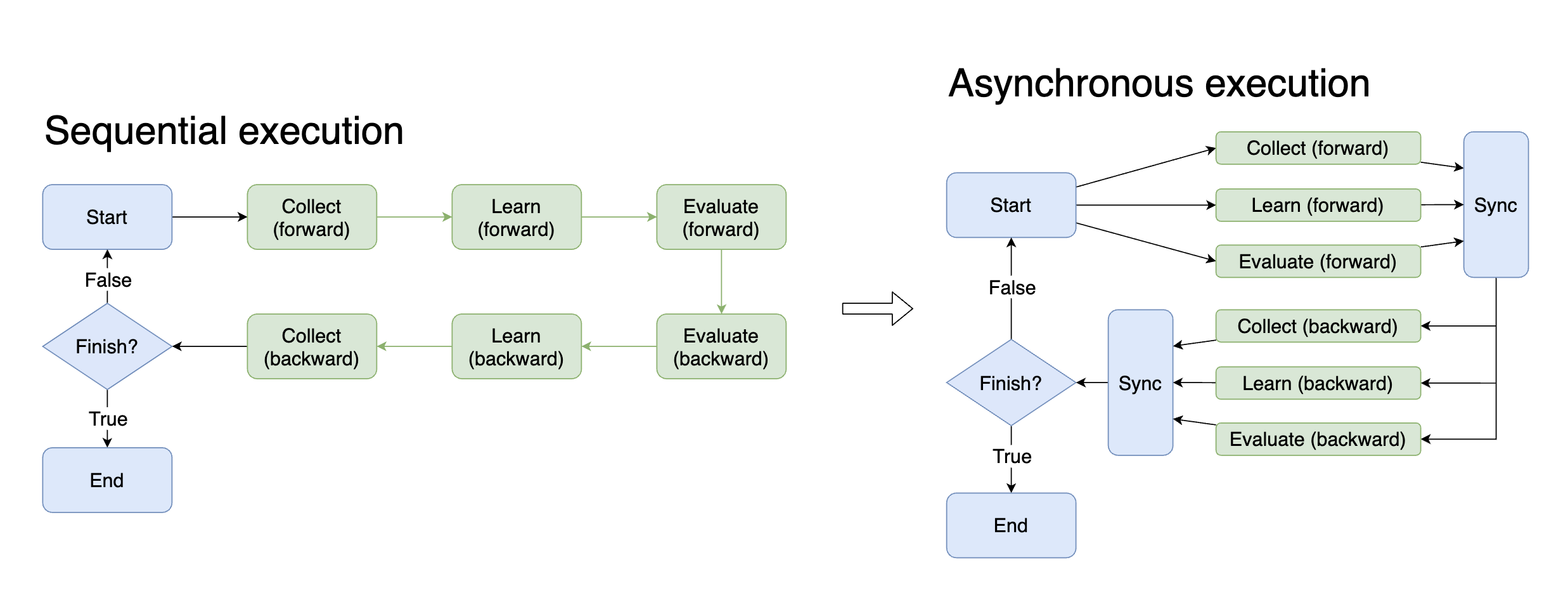
在分秒必争的训练环境中,异步带来的好处是显而易见的。如果能在训练模型时(GPU 密集工作)采集下一次训练的数据(CPU 密集工作),理论上可以将训练时间缩短一半。 而要实现这种异步,则需要控制复杂的流程,小心翼翼的维护各种状态。现在借助中间件和 task,只需更改一个参数,即可实现各个环节的异步。
# 顺序执行
with task.start(async_mode=False, ctx=OnlineRLContext()):
...
# 异步执行
with task.start(async_mode=True, ctx=OnlineRLContext()):
...
除了训练和采集,有很多环节都可以利用异步的好处,例如在训练模型时,将下一批数据提前搬到 GPU 上;在训练模型的同时评估历史模型的表现。 实践中不妨多尝试一下通过异步执行来加速整个交互流程。
不同阶段的中间件¶
大部分中间件都可以对应不同的阶段,您可以通过下图查看已有的中间件与阶段的对应关系,以便正确的组合各类中间件: