Pendulum¶
Overview¶
The inverted pendulum problem is a classic control problem in reinforcement learning. Pendulum is a continuous control task in the inverted pendulum problem. The pendulum starts at a random position and the goal is to swing up to stay upright. As shown below.

Install¶
Installation Method¶
The Pendulum environment is built into the gym, and you can install the gym directly. Its environment id is Pendulum-v1 .
pip install gym
Verify Installation¶
Run the following Python program, if no error is reported, the installation is successful.
import gym
env = gym.make('Pendulum-v1')
obs = env.reset()
print(obs)
Environment Introduction¶
Action Space¶
The action space of Pendulum belongs to the continuous action space.
Control torque: The size range is[-2, 2].
Using the gym environment space definition can be expressed as:
action_space = spaces.Box(low=-2,high=2)
State Space¶
The state space of Pendulum has 3 elements that describe the angle and angular velocity of the pendulum. They are:
sin: The sin value of the angle the pendulum deviates from the vertical direction, the range is[-1, 1].cos: The cos value of the angle the pendulum deviates from the vertical direction, the range is[-1, 1].thetadot: Angular angle of the pendulum, in the range[-8, 8].
Reward Space¶
First calculate cost , including three terms:
angle_normalize(th)**2: Penalty for the angle difference between the current pendulum and the target position0.1*thdot**2: Penalty for angular velocity. Avoid approaching the target while still having a large angular velocity, thus overshooting the target position.0.001*(u**2): Penalty for input torque. The bigger the moment we use, the bigger the penalty.
Add the three terms to get cost . Finally, the inverse of cost , which is -cost , is returned as the reward value.
Termination Condition¶
The termination condition for each episode of the Pendulum environment is any of the following:
Reach the maximum step of the episode.
Other¶
Store Video¶
Some environments have their own rendering plugins. DI-engine does not support the rendering plug-in that comes with the environment, but generates video recordings by saving the logs during training. For details, please refer to the Visualization & Logging section under the DI-engine official documentation Quick start chapter.
DI-zoo Runnable Code Example¶
The following provides a complete Pendulum environment config, using the DDPG algorithm as the policy. Please run the pendulum_ddpg_main.py file in the DI-engine/dizoo/classic_control/pendulum/entry directory, as follows.
import os
import gym
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
from ding.config import compile_config
from ding.worker import BaseLearner, SampleSerialCollector, InteractionSerialEvaluator, AdvancedReplayBuffer
from ding.envs import BaseEnvManager, DingEnvWrapper
from ding.policy import DDPGPolicy
from ding.model import QAC
from ding.utils import set_pkg_seed
from dizoo.classic_control.pendulum.envs import PendulumEnv
from dizoo.classic_control.pendulum.config.pendulum_ddpg_config import pendulum_ddpg_config
def main(cfg, seed=0):
cfg = compile_config(
cfg,
BaseEnvManager,
DDPGPolicy,
BaseLearner,
SampleSerialCollector,
InteractionSerialEvaluator,
AdvancedReplayBuffer,
save_cfg=True
)
# Set up envs for collection and evaluation
collector_env_num, evaluator_env_num = cfg.env.collector_env_num, cfg.env.evaluator_env_num
collector_env = BaseEnvManager(
env_fn=[lambda: PendulumEnv(cfg.env) for _ in range(collector_env_num)], cfg=cfg.env.manager
)
evaluator_env = BaseEnvManager(
env_fn=[lambda: PendulumEnv(cfg.env) for _ in range(evaluator_env_num)], cfg=cfg.env.manager
)
# Set random seed for all package and instance
collector_env.seed(seed)
evaluator_env.seed(seed, dynamic_seed=False)
set_pkg_seed(seed, use_cuda=cfg.policy.cuda)
# Set up RL Policy
model = QAC(**cfg.policy.model)
policy = DDPGPolicy(cfg.policy, model=model)
# Set up collection, training and evaluation utilities
tb_logger = SummaryWriter(os.path.join('./{}/log/'.format(cfg.exp_name), 'serial'))
learner = BaseLearner(cfg.policy.learn.learner, policy.learn_mode, tb_logger, exp_name=cfg.exp_name)
collector = SampleSerialCollector(
cfg.policy.collect.collector, collector_env, policy.collect_mode, tb_logger, exp_name=cfg.exp_name
)
evaluator = InteractionSerialEvaluator(
cfg.policy.eval.evaluator, evaluator_env, policy.eval_mode, tb_logger, exp_name=cfg.exp_name
)
replay_buffer = AdvancedReplayBuffer(cfg.policy.other.replay_buffer, tb_logger, exp_name=cfg.exp_name)
# Training & Evaluation loop
while True:
# Evaluate at the beginning and with specific frequency
if evaluator.should_eval(learner.train_iter):
stop, reward = evaluator.eval(learner.save_checkpoint, learner.train_iter, collector.envstep)
if stop:
break
# Collect data from environments
new_data = collector.collect(train_iter=learner.train_iter)
replay_buffer.push(new_data, cur_collector_envstep=collector.envstep)
# Train
for i in range(cfg.policy.learn.update_per_collect):
train_data = replay_buffer.sample(learner.policy.get_attribute('batch_size'), learner.train_iter)
if train_data is None:
break
learner.train(train_data, collector.envstep)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(pendulum_ddpg_config, seed=0)
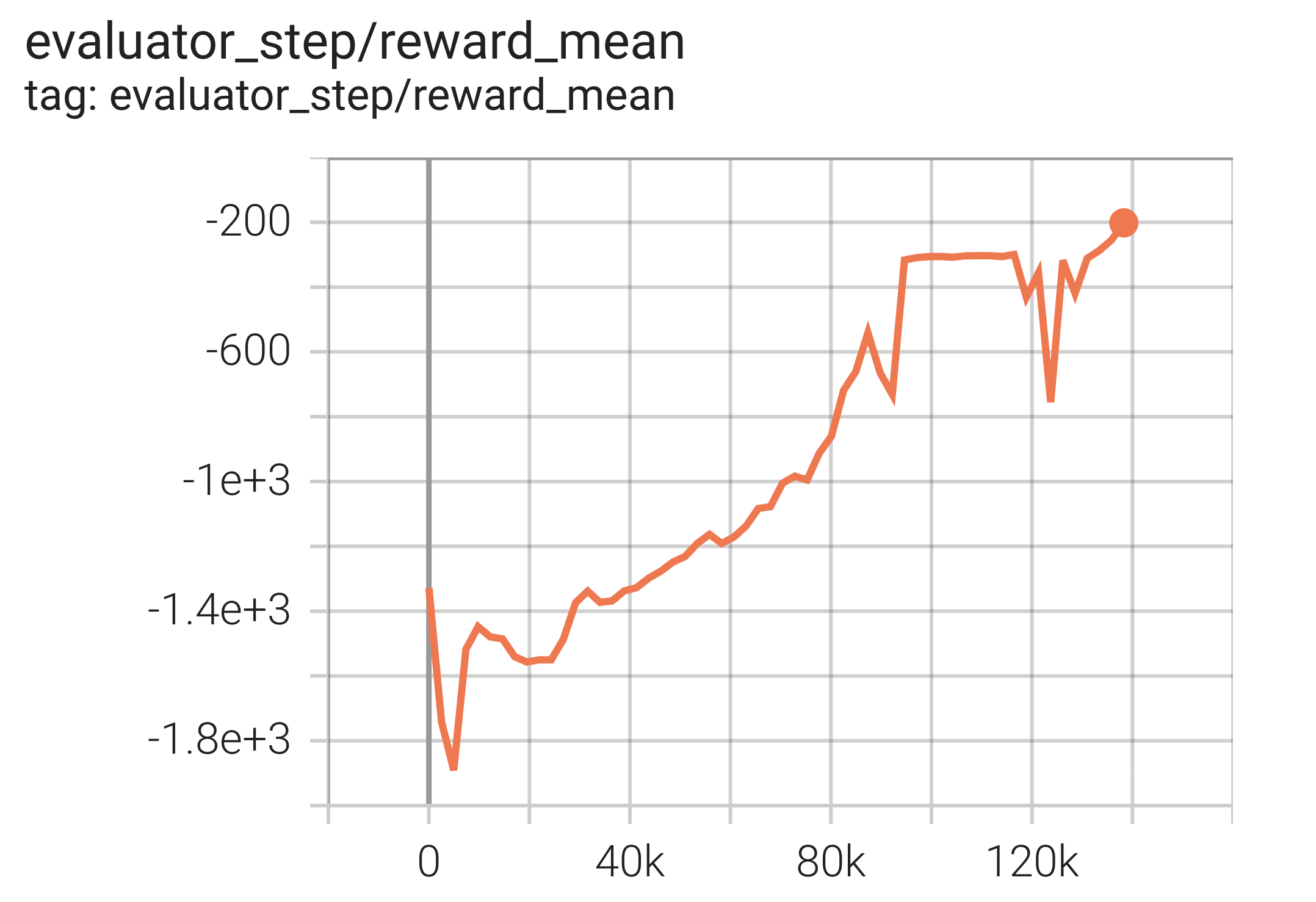
Experimental Results¶
The experimental results using the DDPG algorithm are as follows. The abscissa is episode , and the ordinate is reward_mean .
References¶
Pendulum source code