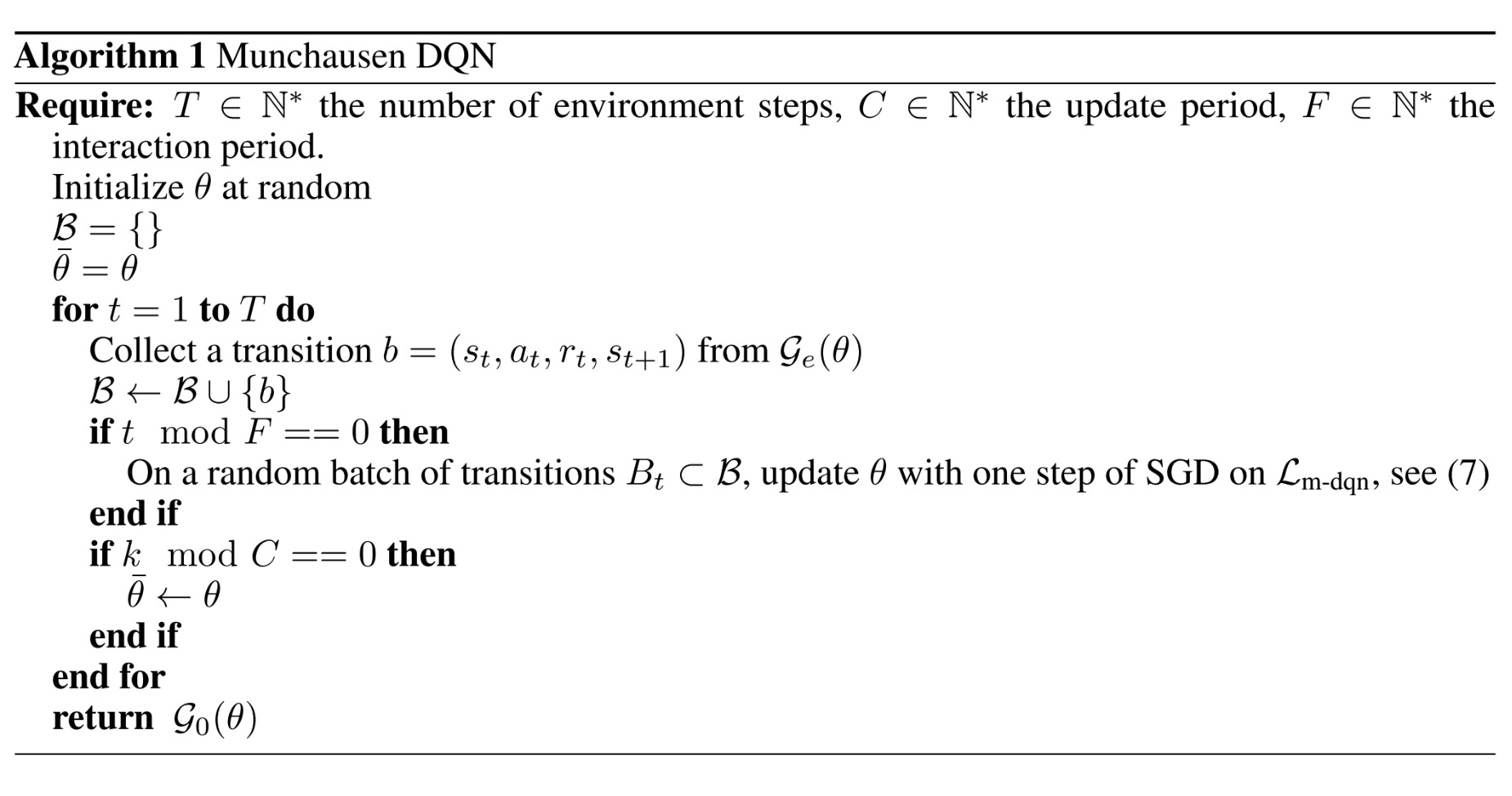
MDQN¶
概述¶
MDQN 是在 Munchausen Reinforcement Learning 中提出的。 作者将这种通用方法称为 “Munchausen Reinforcement Learning” (M-RL), 以纪念 Raspe 的《吹牛大王历险记》中的一段著名描写, 即 Baron 通过拉自己的头发从沼泽中脱身的情节。 从实际使用的角度来看, MDQN 和 DQN 之间的关键区别是 Soft-DQN (传统 DQN 算法的扩展)的即时奖励中添加了一个缩放的 log-policy 。
核心要点¶
1。 MDQN 是一种 无模型 (model-free) 且 基于值函数 (value-based) 的强化学习算法。
2。 MDQN 只支持 离散 (discrete) 动作空间。
3。 MDQN 是一个 异策略 (off-policy) 算法。
4。 MDQN 使用 epsilon贪心 (eps-greedy) 来做探索 (exploration)。
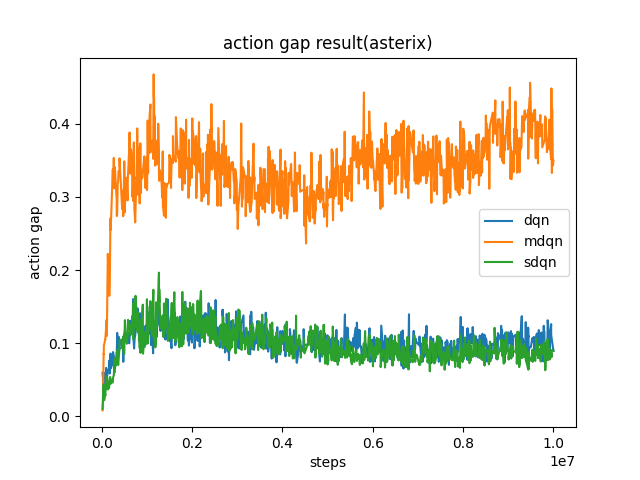
5。 MDQN 增加了 动作间隔 (action gap) , 并具有隐式的 KL正则化 (KL regularization) 。
关键方程或关键框图¶
MDQN 中使用的目标 Q 值 (target Q value) 是:
我们使用以下公式计算 log-policy 的值: \(\alpha \tau \ln \pi_{\bar{\theta}}\left(a_t \mid s_t\right)\)
其中 \(q_k\) 在我们的代码中表示为 target_q_current 。 对于最大熵部分 \(\tau \ln \pi_{\bar{\theta}}\left(a^{\prime} \mid s_{t+1}\right)\) 我们使用相同的公式进行计算,其中 \(q_{k+1}\) 在我们的代码中表示为 target_q 。
我们将 \(\tau \ln \pi(a \mid s)\) 替换为 \([\tau \ln \pi(a \mid s)]_{l_0}^0`\) 因为对数策略项 (log-policy term) 是无界的, 如果策略变得过于接近确定性策略 (deterministic policy) ,可能会导致数值性问题 (numerical issues) 。
同时还将 \(\pi_{\bar{\theta}}\left(a^{\prime} \mid s_{t+1}\right)\) 替换为 \(softmax(q-v)\) ,因为这是在官方实现中使用的方法,但他们并未在论文中提及。
我们使用上述改动后的配置在 asterix 进行测试,得到了与原论文相同的结果, 即MDQN可以增加动作间隙 (action gap) 。
伪代码¶
扩展¶
TBD
实现¶
MDQNPolicy 的默认配置如下:
- class ding.policy.mdqn.MDQNPolicy(cfg: EasyDict, model: Module | None = None, enable_field: List[str] | None = None)[source]
- Overview:
Policy class of Munchausen DQN algorithm, extended by auxiliary objectives. Paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14430.
- Config:
ID
Symbol
Type
Default Value
Description
Other(Shape)
1
typestr
mdqn
RL policy register name, refer toregistryPOLICY_REGISTRYThis arg is optional,a placeholder2
cudabool
False
Whether to use cuda for networkThis arg can be diff-erent from modes3
on_policybool
False
Whether the RL algorithm is on-policyor off-policy4
prioritybool
False
Whether use priority(PER)Priority sample,update priority5
priority_IS_weightbool
False
Whether use Importance Sampling Weightto correct biased update. If True,priority must be True.6
discount_factorfloat
0.97, [0.95, 0.999]
Reward’s future discount factor, aka.gammaMay be 1 when sparsereward env7
nstepint
1, [3, 5]
N-step reward discount sum for targetq_value estimation8
learn.updateper_collect_gpuint
1
How many updates(iterations) to trainafter collector’s one collection. Onlyvalid in serial trainingThis args can be varyfrom envs. Bigger valmeans more off-policy10
learn.batch_sizeint
32
The number of samples of an iteration11
learn.learning_ratefloat
0.001
Gradient step length of an iteration.12
learn.target_update_freqint
2000
Frequence of target network update.Hard(assign) update13
learn.ignore_donebool
False
Whether ignore done for target valuecalculation.Enable it for somefake termination env14
collect.n_sampleint
4
The number of training samples of acall of collector.It varies fromdifferent envs15
collect.unroll_lenint
1
unroll length of an iterationIn RNN, unroll_len>116
other.eps.typestr
exp
exploration rate decay typeSupport [‘exp’,‘linear’].17
other.eps.startfloat
0.01
start value of exploration rate[0,1]18
other.eps.endfloat
0.001
end value of exploration rate[0,1]19
other.eps.decayint
250000
decay length of explorationgreater than 0. setdecay=250000 meansthe exploration ratedecay from startvalue to end valueduring decay length.20
entropy_taufloat
0.003
the ration of entropy in TD loss21
alphafloat
0.9
the ration of Munchausen term to theTD loss
MDQN 使用的 TD error 接口定义如下:
- ding.rl_utils.td.m_q_1step_td_error(data: ~collections.namedtuple, gamma: float, tau: float, alpha: float, criterion: <module 'torch.nn.modules' from '/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.18/x64/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/__init__.py'> = MSELoss()) Tensor[source]
- Overview:
Munchausen td_error for DQN algorithm, support 1 step td error.
- Arguments:
data (
m_q_1step_td_data): The input data, m_q_1step_td_data to calculate lossgamma (
float): Discount factortau (
float): Entropy factor for Munchausen DQNalpha (
float): Discount factor for Munchausen termcriterion (
torch.nn.modules): Loss function criterion
- Returns:
loss (
torch.Tensor): 1step td error, 0-dim tensor
- Shapes:
data (
m_q_1step_td_data): the m_q_1step_td_data containing [‘q’, ‘target_q’, ‘next_q’, ‘act’, ‘reward’, ‘done’, ‘weight’]q (
torch.FloatTensor): \((B, N)\) i.e. [batch_size, action_dim]target_q (
torch.FloatTensor): \((B, N)\) i.e. [batch_size, action_dim]next_q (
torch.FloatTensor): \((B, N)\) i.e. [batch_size, action_dim]act (
torch.LongTensor): \((B, )\)reward (
torch.FloatTensor): \(( , B)\)done (
torch.BoolTensor) \((B, )\), whether done in last timestepweight (
torch.FloatTensoror None): \((B, )\), the training sample weight
- Examples:
>>> action_dim = 4 >>> data = m_q_1step_td_data( >>> q=torch.randn(3, action_dim), >>> target_q=torch.randn(3, action_dim), >>> next_q=torch.randn(3, action_dim), >>> act=torch.randint(0, action_dim, (3,)), >>> reward=torch.randn(3), >>> done=torch.randint(0, 2, (3,)), >>> weight=torch.ones(3), >>> ) >>> loss = m_q_1step_td_error(data, 0.99, 0.01, 0.01)
实验 Benchmark¶
environment |
best mean reward |
evaluation results |
config link |
comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Asterix
(Asterix-v0)
|
8963 |
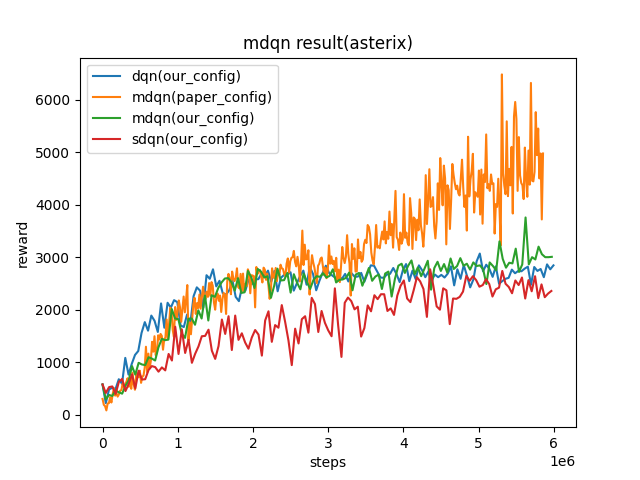
|
sdqn(3513) paper(1718) dqn(3444)
|
|
SpaceInvaders
(SpaceInvaders-v0)
|
2211 |
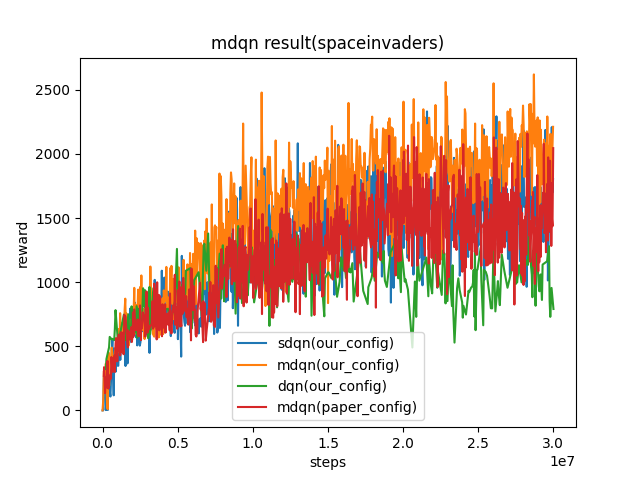
|
sdqn(1804) paper(2045) dqn(1228)
|
|
Enduro
(Enduro-v4)
|
1003 |
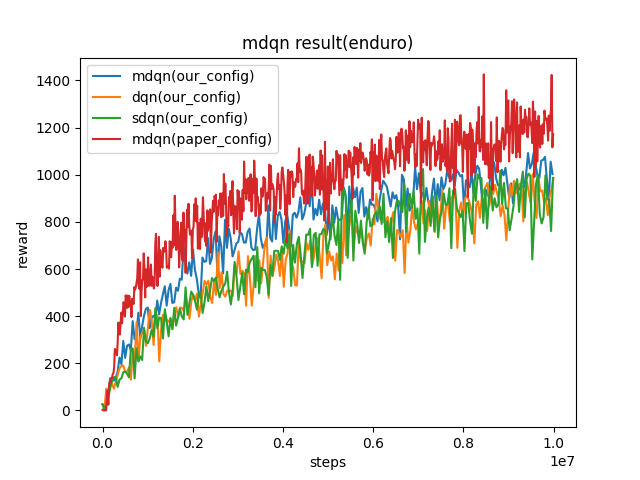
|
sdqn(986.1) paper(1171) dqn(986.4)
|
我们的配置和论文中的配置的主要区别如下:
我们收集了100个样本,进行了十次训练。而在原论文中,收集了4个样本,进行了一次训练。
我们每500个迭代更新一次目标网络 (target network) ,而原论文每2000个迭代更新一次目标网络。
我们用于探索的epsilon从1逐渐下降到0.05,而原论文的epsilon是从0.01到0.001。
P.S.:
以上结果是在 seed 0 上运行同样配置得到的。
对于像DQN这样的离散动作空间算法, 一般采用Atari环境集来进行测试, Atari 环境一般通过10M
env_step的最高均值奖励(highest mean reward)训练来评估。关于Atari环境的更多细节请参考: Atari 环境教程
参考文献¶
Vieillard, Nino, Olivier Pietquin, and Matthieu Geist. “Munchausen reinforcement learning.” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33 (2020): 4235-4246.