QMIX¶
概述¶
QMIX 是由 Rashid et al.(2018) 提出的,用于在多智能体集中式训练中学习基于全局状态信息的联合动作价值函数,并从集中式端到端框架中提取分布式执行策略。 QMIX 使用集中式神经网络来估计联合动作值,作为基于局部观察的每个智能体动作值的复杂非线性组合,这为集中式动作价值函数提供了一种新的表示,并保证了集中式和分散式策略之间的一致性。
QMIX 是 VDN(Sunehag et al. 2017) 的非线性扩展。 与 VDN(Value-Decomposition Networks For Cooperative Multi-Agent Learning ) 相比,QMIX 在训练过程中可以通过超网络(hyper-network)输入的全局信息表示更多的额外状态信息(智能体观测范围外),并且可以表示更丰富的动作价值函数类。
核心要点¶
QMIX 使用 集中式训练与分散式执行(centralized training with decentralized execution) 的范式。
QMIX 是一种 无模型(model-free)、基于价值(value-based)、异策略(off-policy)、多智能体(multi-agent) 的强化学习方法。
QMIX 仅支持 离散(discrete) 动作空间。
QMIX 考虑了一种 部分可观察(partially observable) 的情景,其中每个智能体只获得个体观察。
QMIX 接受 DRQN 作为个体价值网络来解决 部分可观察 问题。
QMIX 使用由 智能体网络(agent networks)、混合网络(mixing network)、超网络(hyper-network) 组成的架构来表示联合价值函数。 混合网络是一个前馈神经网络,它将智能体网络的输出作为输入并单调地混合它们,产生联合动作值。 混合网络的权重由单独的超网络产生。
关键方程或关键图形¶
VDN 和 QMIX 是使用将联合动作价值函数 \(Q_{tot}\) 分解为用于分散执行的个体函数 \(Q_a\) 的思想的代表性方法。
为了实现集中式训练与分散式执行 (centralized training with decentralized execution CTDE),我们需要确保在 \(Q_{tot}\) 上执行的全局 \(argmax\) 与在每个 \(Q_a\) 上执行的一组单独的 \(argmax\) 操作产生相同的结果:
VDN 将联合动作价值函数分解为个体动作价值函数之和。 \($Q_{\mathrm{tot}}(\boldsymbol{\tau}, \boldsymbol{u})=\sum_{i=1}^{N} Q_{i}\left(\tau_{i}, u_{i}\right)$\)
QMIX 扩展了这种加法值分解,将联合动作价值函数表示为一个单调函数。QMIX 基于单调性,即对联合动作值 \(Q_{tot}\) 和个体动作值 \(Q_a\) 之间关系的约束。
QMIX 的整体架构包括个体智能体网络、混合网络和超网络:
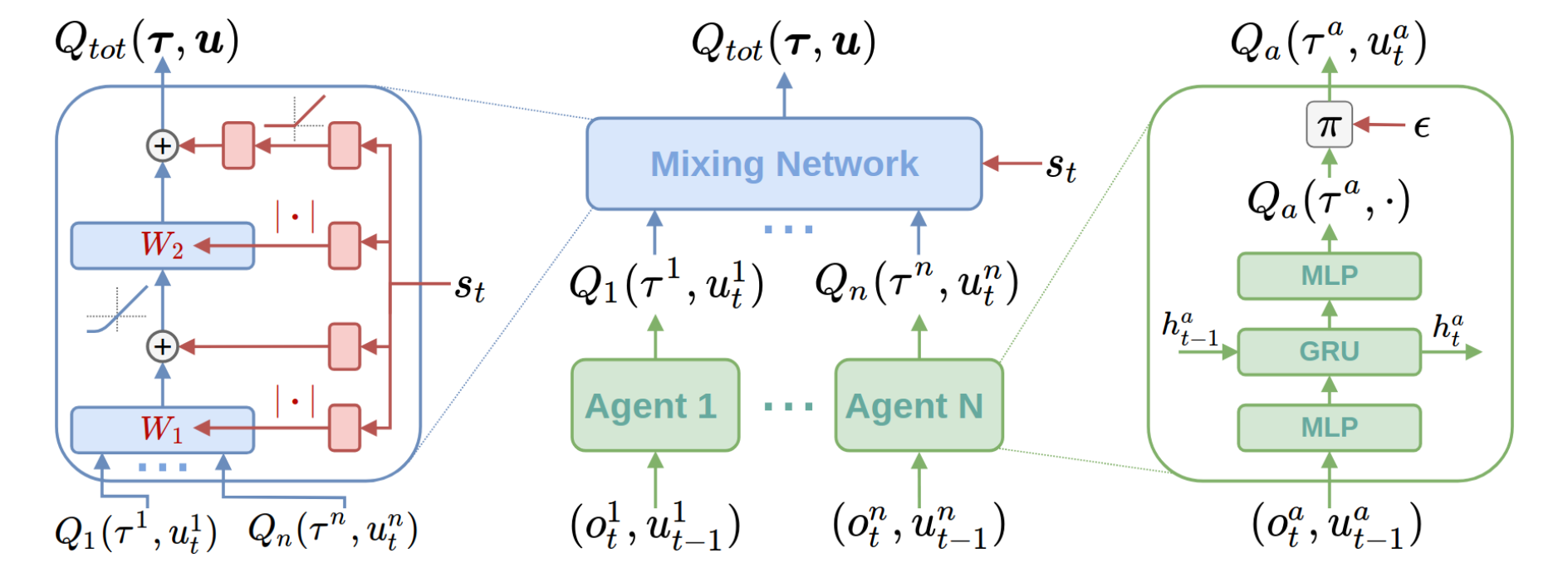
QMIX 通过最小化下面的损失函数来训练混合网络:
混合网络的每个权重都是由独立的超网络产生的,它以全局状态作为输入并输出混合网络一层的权重。更多细节可以在原始论文 Rashid et al.(2018) 中找到。
VDN 和 QMIX 是试图分解 \(Q_tot\) 的方法,分别假设可加性和单调性。因此,满足这些条件的联合动作价值函数将被 VDN 和 QMIX 很好地分解。 然而,存在一些任务,其联合动作价值函数不满足所述条件。 QTRAN (Son et al. 2019) 提出了一种通过将原始联合动作价值函数转换为容易分解的函数来摆脱这种结构约束的分解方法。 QTRAN (QTRAN: Learning to Factorize with Transformation for Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning) 保证了比 VDN 或 QMIX 更一般的分解。
实现¶
算法的默认设置如下:
- class ding.policy.qmix.QMIXPolicy(cfg: EasyDict, model: Module | None = None, enable_field: List[str] | None = None)[source]
- Overview:
Policy class of QMIX algorithm. QMIX is a multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithm, you can view the paper in the following link https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.11485.
- Config:
ID
Symbol
Type
Default Value
Description
Other(Shape)
1
typestr
qmix
POLICY_REGISTRY2
cudabool
True
3
on_policybool
False
prioritybool
False
5
priority_IS_weightbool
False
6
learn.update_per_collectint
20
7
learn.target_update_thetafloat
0.001
8
learn.discount_factorfloat
0.99
QMIX 使用的网络接口定义如下:
- class ding.model.template.QMix(agent_num: int, obs_shape: int, global_obs_shape: int | List[int], action_shape: int, hidden_size_list: list, mixer: bool = True, lstm_type: str = 'gru', activation: Module = ReLU(), dueling: bool = False)[source]
- Overview:
The neural network and computation graph of algorithms related to QMIX(https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.11485). The QMIX is composed of two parts: agent Q network and mixer(optional). The QMIX paper mentions that all agents share local Q network parameters, so only one Q network is initialized here. Then use summation or Mixer network to process the local Q according to the
mixersettings to obtain the global Q.- Interface:
__init__,forward.
- forward(data: dict, single_step: bool = True) dict[source]
- Overview:
QMIX forward computation graph, input dict including time series observation and related data to predict total q_value and each agent q_value.
- Arguments:
- data (
dict): Input data dict with keys [‘obs’, ‘prev_state’, ‘action’].
agent_state (
torch.Tensor): Time series local observation data of each agents.global_state (
torch.Tensor): Time series global observation data.prev_state (
list): Previous rnn state forq_network.action (
torch.Tensoror None): The actions of each agent given outside the function. If action is None, use argmax q_value index as action to calculateagent_q_act.single_step (
bool): Whether single_step forward, if so, add timestep dim before forward and remove it after forward.- Returns:
ret (
dict): Output data dict with keys [total_q,logit,next_state].- ReturnsKeys:
total_q (
torch.Tensor): Total q_value, which is the result of mixer network.agent_q (
torch.Tensor): Each agent q_value.next_state (
list): Next rnn state forq_network.- Shapes:
agent_state (
torch.Tensor): \((T, B, A, N)\), where T is timestep, B is batch_size A is agent_num, N is obs_shape.global_state (
torch.Tensor): \((T, B, M)\), where M is global_obs_shape.prev_state (
list): math:(B, A), a list of length B, and each element is a list of length A.action (
torch.Tensor): \((T, B, A)\).total_q (
torch.Tensor): \((T, B)\).agent_q (
torch.Tensor): \((T, B, A, P)\), where P is action_shape.next_state (
list): math:(B, A), a list of length B, and each element is a list of length A.
Benchmark¶
environment |
best mean reward |
evaluation results |
config link |
comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|
MMM
|
1 |
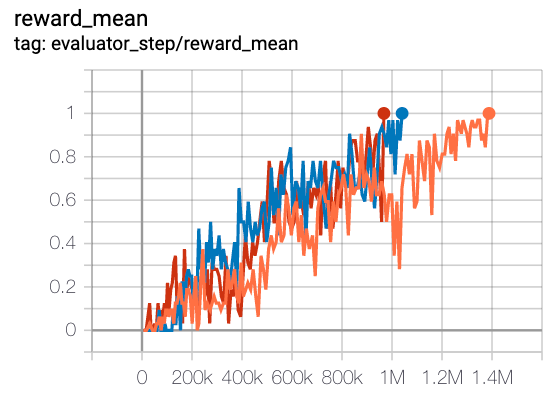
|
Pymarl(1)
|
|
3s5z
|
1 |
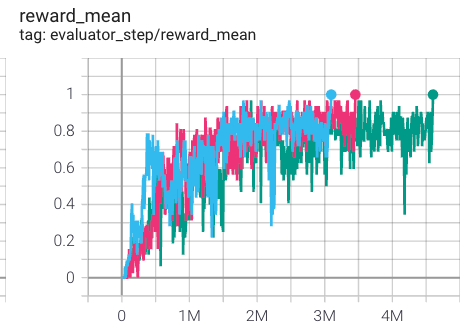
|
Pymarl(1)
|
|
MMM2
|
0.8 |
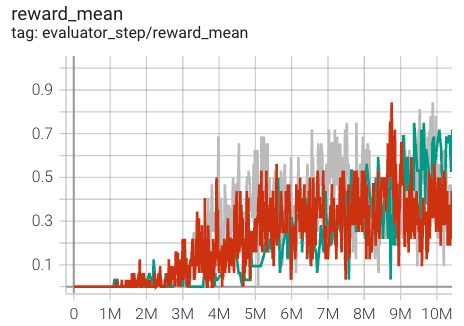
|
Pymarl(0.7)
|
|
5m6m
|
0.6 |
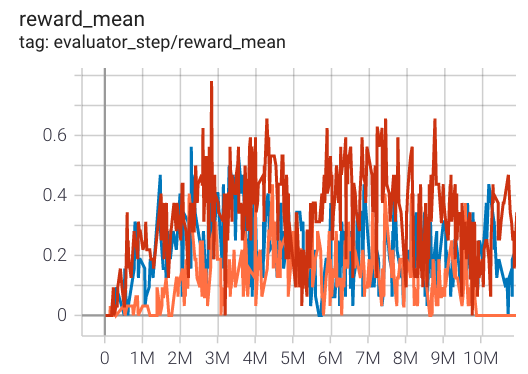
|
Pymarl(0.76)
|
|
2c_vs_64zg
|
1 |
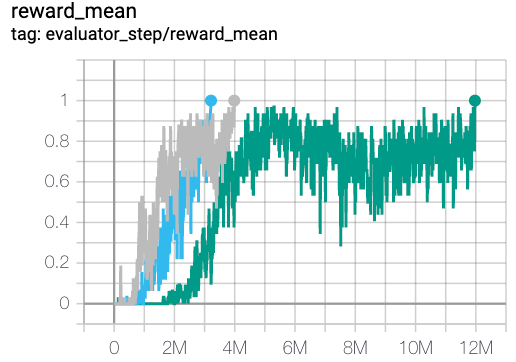
|
Pymarl(1)
|
P.S.:
上述结果是通过在五个不同的随机种子 (0, 1, 2, 3, 4) 上运行相同的配置获得的。
2. 对于像 QMIX 这样的多智能体离散动作空间算法,通常使用 SMAC 环境集进行测试,并通常通过最高平均奖励训练 10M env_step 进行评估。
有关 SMAC 的更多详细信息,请参阅 SMAC Env 教程 SMAC Env Tutorial 。
引用¶
Tabish Rashid, Mikayel Samvelyan, Christian Schroeder de Witt, Gregory Farquhar, Jakob Foerster, Shimon Whiteson. Qmix: Monotonic value function factorisation for deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2018.
Peter Sunehag, Guy Lever, Audrunas Gruslys, Wojciech Marian Czarnecki, Vinicius Zambaldi, Max Jaderberg, Marc Lanctot, Nicolas Sonnerat, Joel Z. Leibo, Karl Tuyls, Thore Graepel. Value-decomposition networks for cooperative multi-agent learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.05296, 2017.
Kyunghwan Son, Daewoo Kim, Wan Ju Kang, David Earl Hostallero, Yung Yi. QTRAN: Learning to Factorize with Transformation for Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2019.
Mikayel Samvelyan, Tabish Rashid, Christian Schroeder de Witt, Gregory Farquhar, Nantas Nardelli, Tim G. J. Rudner, Chia-Man Hung, Philip H. S. Torr, Jakob Foerster, Shimon Whiteson. The StarCraft Multi-Agent Challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.04043, 2019.